Placenta previa, also called as low-lying placenta, that happens when the placenta conceals a specific part or all of the part of the cervix in the later stages of pregnancy. This condition results in severe bleeding prior or at the time of labor. In this article, we will learn about the different types of Placenta Previa, its causes, signs, and method of treatment.
What is the cause of Placenta Previa?
When a woman gets pregnant, then her body begins to form a placenta in the uterus. It is a sac-like organ that supplies the necessary nutrition and oxygen to the baby and eliminates undesirable elements from the blood of the baby. This organ gets detached and removed after the birth of the baby.
In initial stages of pregnancy, the placenta lies at lower region in the uterus. As the pregnancy proceeds, and the uterus stretches, it begins to displace from its position and move upward in the uterus. By the end of third trimester, the placenta is closer to the top region of the womb. In this state, the cervix starts to expand and provide a clear path for the delivery of the baby.
When the placenta attaches to the cervix partially or completely during the later months of pregnancy, then this condition is termed as “placenta previa”. In such a situation, a woman needs constant bed rest.
Signs associated with Placenta Previa
The primary sign of Placenta Previa is minimal vaginal spotting to heavy vaginal bleeding. Other signs include:
- Excruciating pains
- Recurrent bleeding that happen periodically with a gap of a week
- Bleeding after sexual intercourse
- Bleeding in the second trimester of pregnancy
Who are at more risk of developing this condition?
Women who can relate to below conditions are more prone to developing Placenta Previa.
- Unfamiliar position of the baby i.e., breech or transverse
- Previous uterus surgeries that includes removal of uterine fibroids, cesarean delivery, dilation, curettage
- Large-sized placenta
- Abnormal shape of uterus
- History of miscarriage
- History of Placenta Previa
- Older than 35
- Have been pregnant with twin babies or multiples
- Belongs to Asian community
- Being a smoker
Diagnosis of Placenta Previa
Placenta previa will begin in the 20th week of ultrasound scan. Mostly, at this time, the placement of placenta is lower in the uterus. Over time, the placenta comes to its normal position. Only ten percentage of cases develop into full placenta previa. If you experience bleeding in the later stages of the pregnancy, then following methods are performed to examine the placement of the placenta:
- Transvaginal ultrasound: This method is viewed to be the most accurate method to determine the exact position of the placement. It provides an internal view of the cervix, and vaginal canal.
- Transabdominal ultrasound: This procedure comprises of a using a transducer around the abdomen region to give the picture of the pelvic organs.
- Magnetic resonance imaging: This scan clearly determines the location of placenta in the body.
Also read: Reasons for a C-Section Birth
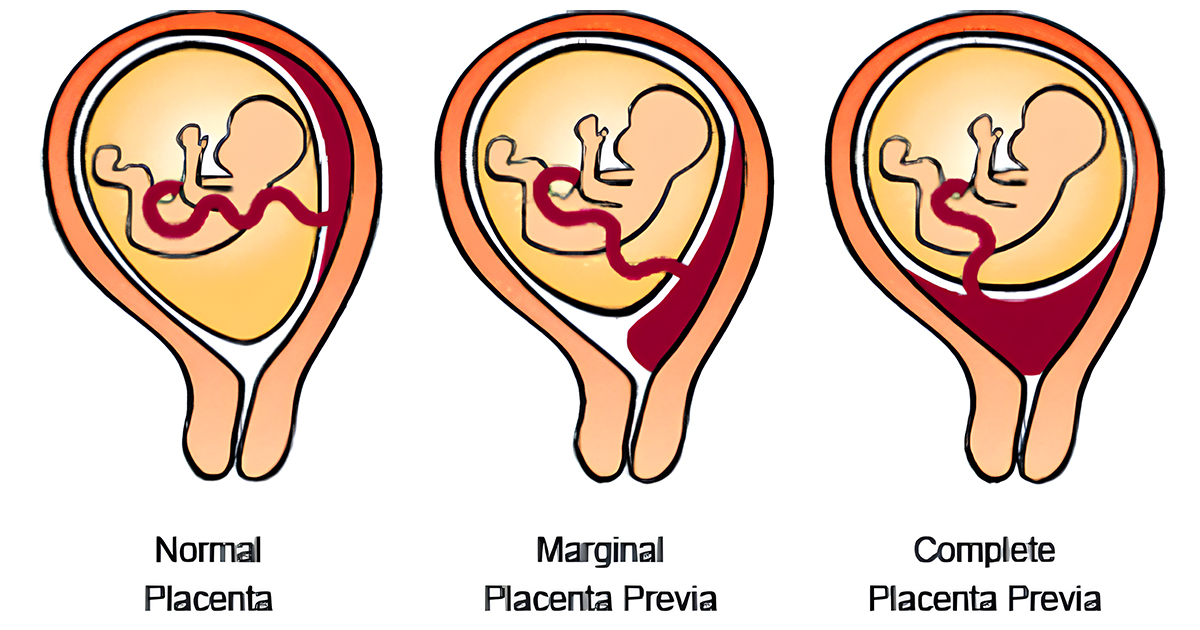
Different types of Placenta Previa
Your doctor will first determine the type of placenta previa and based on that will prescribe the treatment.
- Partial Placenta Previa: This type covers the entrance of the cervix in a partial way. There is a possibility of vaginal birth.
- Low-Lying Placenta Previa: In this case, the placenta gets placed at the corner of the cervix. Here, in this case also a vaginal delivery is possible.
- Marginal Placenta Previa: In this case, the placenta starts to develop at the bottom region of the uterus. The placenta would not cover the cervix. The edge of the placenta touches the entrance of the cervix and may cause some bleeding during labor. This type also leads to safe vaginal births.
- Major Placenta Previa: This is serious type of Placenta Previa where the placenta completely covers the entire cervix region. In such a case, C-section delivery is recommended. In some cases, it can also cause a baby to deliver prematurely.
Treatment of Placenta Previa
Based on the type of Placenta Previa and the extent of bleeding, your doctors will decide the right method to treat this condition.
- No or very less bleeding: In such a case bed rest is advised to the expecting mother. You should sit, and stand only when it is absolutely necessary. Avoid sex and exercise.
- Excessive bleeding: In this case, a woman is advised for a complete bed rest in hospital. Blood transfusions can be performed to compensate for the blood loss. C-section delivery is scheduled by the doctor. Along with it, corticosteroid injections are given to the baby to enhance development of lungs.
- Uncontrollable bleeding: When the bleeding is unstoppable, your doctor will advise you for an emergency cesarean delivery.
Conclusion
Placenta Previa occurs in different types in the body. Each of these types affects the delivery in a different way. If you find any of the above-mentioned signs, then get immediate assistance of the medical professional.